30 Morphological, Serological and Biochemical Methods
Introduction:
Paternity means fatherhood. Now a day’s more paternity disputes are arising. Paternity dispute relations involve domestic relations like, to deal in divorce cases. When a child is born after divorce or before the date of marriage. When third party is alleged to be father of one of the children is called putative father. This can arise in the case of infertility, extra marital affairs, or to claim the property from father. So things can be solved by the analysis of the blood group, DNA analysis. Saliva is useful sources for DNA genetic studies analysis in settlement of paternity dispute. In this chapter we will discuss the morphology, serology and biochemical approaches to solve paternity dispute. Some of the tests are ordered by the court to prove of paternity like polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Short Tandem Repeat (STR), DNA test.
1.1. Morphology deals with the branch of biology which deals with internal and external structure of an organism. It’s divided into two parts that is: i). Anatomy, ii) Eidonomy.
Anatomy deals with the structure, shape and relationship of any part of the body of an organisms. While Eidonomy is concerned with the external morphology of an organisms. Morphology includes like hair, face, dental morphology, hand morphology, skull, chromosome,
1.2. Morphology of human hair.
The origin of hair include root, shaft and a tip end.
1. Root presents in the skin enclosed by the hair follicles. Hair can be examine from naturally fallen hair or hair pulled away by force.
i. If the hair root is found with the dead root, it can be said that it’s fallen naturally.
ii. If the hair roots are leaving and bulbous in nature so it can be said that hair has been pulled away by force.
iii. If the hair roots having both dead roots and present of leaving bulbous. So it can be said that hair is pulled by the force.
2. Shaft: the portion of the hair emerging from the root and it’s extended up to tips. Shaft indicates the length and cross section of the hair from where it’s originated. For example, if hair is having three concave sides so this type of hair belongs to the moustache or beard. If oval or kidney shaped, hair belongs to the torso. Head hair having shaft round in shape cross-section sometimes oval in curly shapes.
3. Tips: Extreme upper portion of hair is called tip. Hair cut indicates its state. Stepped or irregular tips are cut hairs having blunt cut. Clean cut tips indicated that hair having sharp cut edges. Such edges are cut from the razors, scissors or blade.
1.2.1 Hair DNA testing:
Hair DNA testing is done by the oral swab. Swab is so simple to use and having success in proving the paternity cases. Forensic expert collects the Hair sample from the place where incident occurs. Hair that is cut or shed down contains the DNA. For cut hair specific test is known as MtDNA (Mitrochondrial DNA test).
1.3. Morphology of human facial skeleton:
The primary bones of the faces are following:
- Mandible: It’s U-Shaped bone. It consist the lower jaw and teeth. Mandible is only bone in facial skeleton which can be moved. It’s used for mastification process.
- Maxilla: Forms the roof for oral cavity and floor to lateral wall and floor to nasal cavity.
- Frontal bone,
- Nasal bone,
- Zygoma.
2. Serology is the properties and effect of serums in analysing blood trace. The evidence of the biological particles in semen, saliva. Faecal matter and perspiration. This all is done to detect the presence of foreign particles in blood. Other foreign particles like presence of the drugs, alcohol or poisons in urine are carried out by specialist in toxicology or chemistry.
Karl Landsteiner in the beginning of the twentieth century demonstrated that serum of persons would agglutinate, the red blood cells contain antigens factors and blood serum contains the antibodies. Two antigens, A and B, were identified with two antibodies i.e. anti-A, and anti-B. So if a person has one of the two antigens so his/her blood type will be A or B. Landsteiner in 1927 also discovered additional blood group known as MN System and in 1940, Rh Blood group. In 1910 scientist discovered that blood groups were having certain traits that are inherited (genetics laws), so it could be used for the case of paternity in criminal investigation. In 1985 major breakthrough in Forensic science occurred through forensic serology. Alec Jeffrey and his colleagues discovered the DNA structure.
2.1. Physical properties of Blood:
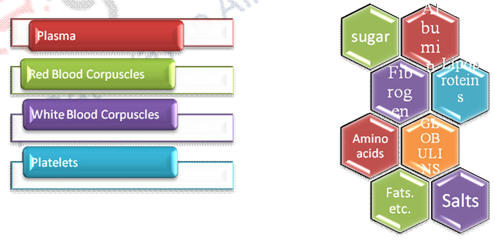
1. Blood is specialized tissue of human body. The main function of blood is to supply nourishment especially oxygen to the cellular elements of the tissue of the other parts. Removing the waste products of the metabolic activities, especially carbon dioxide. It maintains the required temperature of the body, proper balance of the fluid substances in the human body. Blood circulate through heart, arteries, capillaries and vein. It consists of plasma, RBC, WBC, platelets. Blood colour is red due to the presence of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin binds the oxygen in the inhaled air in the lungs. Plasma is liquid part in blood mixtures, while RBC, WBC and platelets are solids parts. Clotting of the blood takes place due to separation of fibrin from plasma. Then liquid left behind is called serum. Generally human body consists of five and half litres of the blood.
Due to duration of time on exposure of the blood its colour gets changed. Cells structures get destroyed and protein also loses their characteristics. Fresh blood appears bright red in colour, after twenty hours blood colour becomes brown- red. After twenty four hours it becomes dark brown or black in colour.
2. Drying of blood get affected by the amount of blood, humidity, temperature, light, rain, wind condition, sources of blood stain, nature of surface bearing stains.
3. Frothy blood comes from lungs; Nasal blood comes from nasal mucus and consists of nasal hairs. While vomited blood colour is chocolate. Menstrual blood is dark in colour containing vaginal epithelial cells and endometrial cells. Blood stains on metallic surface seems to rust.
2.2 Significance of Blood group systems.
Blood groups are very useful in identifying the problems of paternity like:
a) To identify blood stains and other body products.
b) To solve the cases of paternity, maternity disputes.
It’s based on the fact that blood groups are inherited according to the Mendel laws. For example in case where putative father and mother of child both having blood group “O” but child blood group is B. So this kind of case can be solved by the Mendel’s first law of inheritance. i.e. Law of segregation.
Second Example when parents are homozygous for any blood group genes. Child of these parents must carry each gene. When father is Rh -ve so each child inherits Rh -ve. Any of the child having Rh type +ve belongs to another father. This case can be solved by the Rhesus system.
2.2.1. Some of the tests to determine the paternity cases they are following: Duffy, Kell, Luteran Lua, MNS, RH and ABO (A1, A2).
- Lutheran Group: Paternity can be accepted only after the first order exclusion. When child is Lu a and antigen is not found in putative father and mother. But it has to be seen very carefully because suppressor gene which inhibits both Lua and Lub is known to occur in Lutheran system. So to prove suppressor gene is working or not must test the family with anti Lub.
- Duffy Blood group: to test the paternity anti fy a antibody is tested with fya antigen. We should be very careful for the presence of the alleles which are negative anti fy a and anti fy b.
- ABO blood groups. This system is very useful since several years in family studies. Only minimal cases show the abnormalities. In case of mutation where mother was A, B, and child group is O. Or in the case where in one generation B gene was suppressed.
2.2.2. In recent years more advance techniques has been developed to determine the paternity i.e.
- Human Leukocyte (HLA): High degree of discrimination of HLA systems make more accurate probability for determining paternity. It caused the revolution in paternity determination after combining HLA with red cells antigens test.
Case 1. For HLA: In a New York court generally accepted, the HLA for paternity dispute in solving the case of Goodrich v. Norman. Court held that alleged father has right to not exclude from the HLA red cells antigen test. Judge of the court found that HLA techniques widely accepted by the scientist. It proved that organ transplant is used to match the donor and recipients. It’s very important when dealing with the lives of the patients.
Case 2. For HLA: In New Jersey Malvasi vs. Malvasi case. Court granted the putative father motions to oblige mother to have HLA testing. Because HLA testing was highly recognised by the scientific community.
- Red cell enzymes and blood serum protein by electrophoresis method: Many Blood serum proteins and red cell enzymes have proven useful in determining the paternity test. By electrophoresis method. Because proteins and enzymes process follow the Mendelian inheritance patterns.
2.3. Analysis of Blood:
Locating blood on objects: If some dark or red stain is found that means it’s blood. Sometimes stains may be very small or on the dark surface of the floor. There are some test to determine the blood stains are: i) Luminol Blood test, ii). Fluorescein test.
Luminol Test: Luminol is reagent which by help of hydrogen peroxide goes to oxidation on alkaline solution in the presence of heme fraction of haemoglobin. Heme Catalyzed the reaction but it doesn’t take part in reaction. Haemoglobin is present in the blood which carries the oxygen and carbon dioxide from cells and to cells.
product of reaction 3-aminophthalanate, goes reaction Chemiluminescene (Chemiluminescence refers to emission of light from a chemical reactions in solid, gas or liquid matters.) After forming the product its emit the lights on its own. So during the crime scene, area is darkened and luminal reagent test is applied there. No extra light need for this. When Luminol reagent is applied it appears too blue to yellow green colour. Which show the presence of the blood. This colour is last for the 30 seconds after applying another reagent.
Fluorescein: Also emits lights when it reacts with oxidant and heme. It undergoes to fluorescence. In the suspected place of the blood stain its applied with hydrogen peroxide. Strong emit light is used to induce fluorescence.
Confirmation of blood test: Luminol and fluroscene are not specifying for the blood. Although it’s very useful for locating on large surface. There are two tests for confirmation of the blood i.e. i) Takayamatest ii) Teichmann test.
Takayama test and Teichmann test both is microcrystalline test. When a crystallined reagent is aaded to suspect blood. A formation of crystal shaped by the reagent and heme is given the confirmatory for the blood.
Blood stain patterns Analysis: Blood stain pattern used to interpret at crime scene to create action that cause the blood shed at different patterns. Blood pattern analysis having some biological, physics and mathematics principle i.e. Behaviour of blood, capillary action, velocity and cohesion, geometry shape and angle through which blood flows.
2.4 Types of stains are basically three types:
- Passive stain: It includes flow, pool and drops. Gravity acting on an injured body.
- Transfer stain: Existing bloodstains and leaving wipes, patterns, swipes of the blood by shoe, print or body dragged so it leaves the smear.
- Projected or impact stains. When the blood projected through air and seen spatter, it includes gushes, splashes and arterial spurts.
2.4 Blood Shed Events:
At Crime scene amount of blood vary depending on the circumstance of the events. The amount of blood force will determine the patterns and volume of blood stains they are following:
- Sharp force injuries (stabbing): it is forcefully cause by object like knife, ice pick. Less blood deposite on instrument so it can be linear patterns of strains
- Gunshot Injuries: Caused by bullets entering and existing through body and live the stains mist like spatters.
- Blunt Force injuries (beating or hitting): Such as hammer, bat.Objects impact the larger surface area collect more blood and having varying size of the blood drops.
a. Blood Evidences are collected are following:
- Sampling blood stains for DNA Profiling. It can be done by swab samples of dried blood and then develop a DNA profile.
- Documentation like photographed of concrete flooring.
2.6 Some others biological stain and fluids like:
- Saliva.
- Vaginal secretions.
- Seminal fluid.
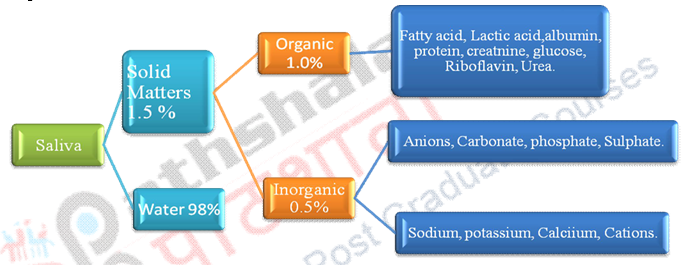
1. Saliva is secret in mouth for digestion of food. It consists of water, proteins, enzymes and salts. Saliva secretion is mostly from sublingual (4%), submandibular (71%), and parotid (25%). These all glands are known as salivary glands. Density of saliva is higher than water and ranges from 1.002 to 1.012. Saliva is slightly acidic in nature (pH 6.02 to 7.05). The solid substances consist of several cells such as epithetical cells, yeast bacteria. Enzymes are ptyalin i.e. lipase, amylase, phosphate etc.
Composition of saliva
Test for saliva is “alpha amylase test’. Alpha amylase is an enzyme useful in breaking the starch present in the food. To identify alpha amylase, the starch- iodide test is used.
Saliva for Paternity Test: Saliva has been proved for the paternity solving cases. Saliva having the good sources for the DNA. In several studies it has been proved that DNA banding obtaining patterns from saliva or saliva stained is good sources. It’s helpful in giving the justice to the victims to proved alleged father to be biological father.
Case report from Lucknow: 24 years old female victim lodged F.I.R in Barabanki police station, that she was raped by the MR.X. a year back. She claimed that she is having 3 months old baby girl by the Mr.X. who raped her. Now she wants the justice and compensation. This case was referred to the Medical Department, Genetics, Sanjay Gandhi post graduate institute of medical science for paternity test. So saliva samples were collected from suspected mother and father, blood and saliva sample from oral cavity of the baby.
2. Vaginal secretions: Test used for vaginal secretions is “glycogenated epithelial cells”. The gycogenated cells are formed during the menstruation cycle and its quantity depends on the menstruation cycle. Menstruation cycle produce the ovulation and ovulation produce highest numbers of glycogenated cells. Glycogenated cells stain with “periodic acid-Schiff reagents’. After staining glycogenated, it gives bright magenta colour.
3. Seminal fluid: Semen is mixture of variety of organic, inorganic, sperms and cells.Sperms consists of head and tails. Head contain DNA from male and tails helps in moving. Semen is a viscous whitish secretion of male reproductive organs contains spermatozoa, and consisting of secretion of testes, prostate, bulbourethal gland and seminal vesicles. The pH level of seminal fluid is 7.2-8.0 is alkaline which help in neutralizing acidic environment of the vagina that cause harm to sperm cells. Zinc presented in prostate secretion is useful in stabilizing the DNA – containing chromatins in the sperms cells. Sperms are made up of Head, Mid piece and Tail.
Head consists of acrosome, nucleus containing chromosomes. Mid pieces consists of mitochondria that provide energy for swimming.
a) Preliminary test for Semen: Is a seminal acid phosphate test. And other is “BrentamineFast Blue B” is major reagent for seminal test.
b) Confirmatory test for semen: A pair of dyes, picroindigocarmine (PIC) and Nuclear fast Red. Both test collectively are known as “A Christmas tree stain’. This test is developed for sperms cells visualization.
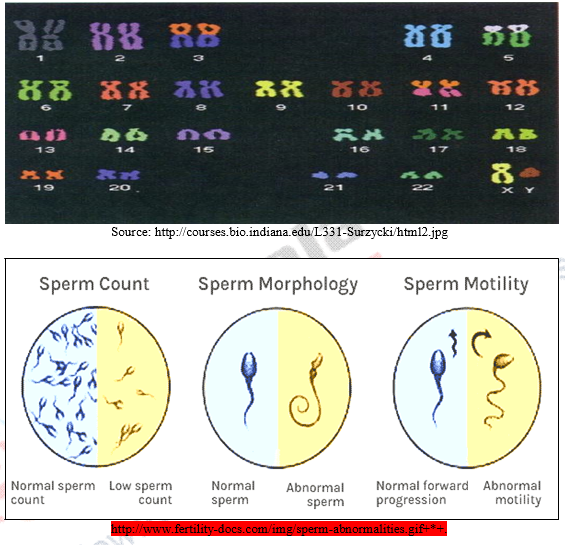
c) Prostate specific antigens: Oligospermic is low sperm count. Aspermic is complete lack of sperm in semen. If a person is prostate specific antigen is found that is p 30. P30 is secreted by prostate gland in semen’s; below the limits of the detection of the test a special antigen body test kit has been developed.
Seminal stains detection test are:
- Acid phosphate test.
- Creatinine in phospokinase.
- Ammonium Molybdatetets.
- Florence Test.
- Barberio Test.
- Semen Specific Gycoprotein (p30) Test.
- Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
- LDM Isoenzyme test.
- Acid Phosphate isoenzyme method:
Acid phosphateisoenzyme method: Its modified method of Fishman and Lerner’s method. After obtaining the fluid through maceration of a small cloth piece is placed in cavity. On a porcelain tile two drops of citrate buffer and 1% W/V aqueous solution of disodium Phenyl phosphate are added. Then after ten minutes by adding two drops of phenol reagent and 2 drops of 20% W/V solution of sodium carbonate the phenol is detected.
Florence Test: few drops of strains are extracted by the watery solution and taken to slide. After obtaining the stain a drop of florescence reagent 8% W/V solution of iodine in water containing 5% W/V of potassium iodide is poured and mix slowly by covering slip. Dark Brown crystal of choline periodide formed in few minutes.
Barberio Test: This test is used for detection of sperm. A few drops of Berberios reagent added to spermatic fluid. Then spermatic fluids produce the crystal of sperm in picrate (needle shaped, rhombic and give yellow colour).
Creatinine phosphokinase: it is beneficial because it can detect the six month old cases of normal seminal fluid.
Choline and Sperminetest: Semen consists of choline and sperm. So dry semen or liquid semen can be detected by the chromatic graphic technique.
2.7. Medical significance of Seminal stains: It will useful for the cases like. Rape, false accusation by the women, incest (sexual intercourse in blood realtiona), sexual murder, Sodomy (Anal intercourse), Bestiality (Sexual intercourse by human being to its lower animal like sheep, dogs etc).
Some place where one can look for semen investigation:
- Seen at crime: on the floor, grasses, roof, car, etc.
- Clothes: Bed sheet, pillow cover, undergarments, trousers, towels.
- Body: Thigh, Vagina, pubic hair and perineum.
3. Biochemical methods Used for detecting Alcohol consumption: Here some of the biomarkers used for alcohol uses they are:
- Gamma- glutamyl transferase (GGT): Its large molecule of glycoprotein consists of protein and carbohydrate helps in digestion found in liver cells in other cells like production of bile including biliary epithelial cells. GGT is early detection for liver disease. Like chronic heavy drinkers, also for them who consume some amount of drugs. GGT only shows the 30-50 percent of excessive drinkers.
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT).
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): Alanine and aspartate are enzyme helps in metabolize amino acids, building blocks of protein. Alanine and aspatate are less sensitive then GGT marker/ they are more useful for detecting liver disease ALT is more specific of alcohol induced liver injury because it is found in liver. While AST found in kidney, heart, brain and liver. Very high level of these enzymes indicate the alcoholic disease.
- Carbohydrate deficient transferring (CDT): CDT is another form of glycoprotein transferring. CDT is molecule responsible for carrying iron within blood stream. Transferring contains 4-6 molecules sialic acid molecules. Heavy drinkers have higher amount of CDT forms in comparison to the normal person.
- Whole Blood associated acetaldehyde (WBAA).
- Mean Corpuscular volume (MCV): This mean person red blood cells are also associated with heavy chronic drinkers. Mean corpuscular volume is useful because it stay high for several months even after persons stop taking of alcohol.
- Fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE): Body produce fatty acid ethyl esters when it breaks down alcohol. It’s found in pancreas, liver and in fat i.e. adipose tissue upto 24 hours of alcohol consumption.
- Salsolinol: Salsolinol is compound. Its formed when alcohols react by product of acetaldehyde or pyruvate (metabolite of glucose that used by cells for energy) with neurotransmitter dopamine (it’s brain chemicals) that communicate information and Dopamine is special neurotransmitter because it consist of both excitatory and inhibitory. There are two kinds of neuro transmitter that is: excitatory and inhibitory. Inhibitary calm the brain, balance the mood and easily depleted when excitatory over reacts. The role of neurotransmitter and dopamine in cognition and movements
- Ethyl glucuronide (EtG): it’s form in liver when alcohol reacts with glucoronic acids. Its detoxify drugs by turning them into water soluble compounds that easily removed from body. EtG can also detect in other body fluids like body tissues, hair. EtG can detect in blood for up to 36 hours. And in Urine for 5 days after heavy drinking’s. If person shows that EtG positive that means person has consume alcohol recently.
3.1. Urine test analysis: Includes chemical test, biochemical test and Gas chromatography. Gas chromatography used widely because like blood test it differentiates the ketones and aldehydes (problems that exist with diabetics peoples with other disorder).
3.2. Methods used for Post Mortem:
3.3. Various Tissues detect the useful substance for post mortem
3.4. Post-mortem Biochemical examination of Synovial fluid includes:
3.5. Post-Morten investigation of death involving asphyxiation and respiratory distress involve some methods they are followings:
- Immuno staining.
- Serum SP- A assay: Performed automated on enzyme immunoassay(ELISA).
- Pulmonary tissue SP –A mRNA assay: It involve the lung tissue specimens were obtained at autopsy. Immediately it dissolved into RNA stabilization solution and stored. From lung tissue homogenate RNA was extracted by using RNA aqueous and assayed for SP-A1/A2 mRNA by using TAQMAN fluorogenic detection system.
3.6. Case study for post-mortem biochemical methods they are following:
- Unexpected fatal diabetic ketoacidosis: The case presented concerns 37 years old man (A) found dead on Friday evening at 9.p.m. in his friend’s (B) apartment. He was staying with him since returning to Switzerland. “B” had said that they both had consumed cocaine by smoking on previous night. On the day of death (A) stayed in all day, he was tired and vomiting many time. On the other hand “B” did not suffer from any problems. On obtaining medical information from his parents it was revealed that “A” was not suffering from any particular disease. Toxicology analyses were performed on blood, hair, urine sample were taken by autopsy. Included blood ethanol determination and screening done for common drugs illegal substance by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. It was found that concentrations of methadone, EDDP, benozoylecgonine, cocaine, codeine and morphine in the subjects hairs. It was resulted that subjects used the cocaine, morphine on the daily basis during the month of preceding his death.
- Primary aldosteronism with intracranial haemorrhage: A case of 48 years old man found dead early in the morning in bedroom by members of his family. Information revealed by the family members was that he was not suffering from any particular disease. The macroscopic external view of the body revealed that no injuries were found. Toxicology analyses resulted that screening for common drugs, illegal substance did not detect any drugs or alcohol use. Then biochemistry investigations were performed on post mortem serum from blood, Urine, Vitreous humor stored in tubes with no preservative. But revealed that in post mortem serum, aldosterone and cortisol level, urine cortisol vitreous sodium, glucose, chlorides were increased. On the basis of biochemical and autopsy it was concluded that the death was due to cerebral haemorrhage. It was also observed that with no signs of vascular malformation or aneurism, tumours and cerebral trauma.
Conclusion: To solve the cases of paternity disputes several techniques have been developed. Presence of the DNA in Saliva, Hair, Blood test, HLA made it easier to solve cases. HLA, red enzyme protein test gives more accurate results to determine paternity. Now a day’s falsely accused putative father can be excluded from paternity in ninety percent of all cases. Most paternity test is done for providing the justice to victims, financial reasons to give legal rights, supports and responsibility for innocents and justice to victims.
| you can view video on Morphological, Serological and Biochemical Methods |