27 Ginger: Dehydrated Ginger
27.1 Dehydrated Ginger
The country of production determines the types of ginger available to spice importers: Indian (Cochin and Calicut), Chinese, African (Nigeria and Sierra Leone), Jamaican, and Australian. Indian (Cochin) and Jamaican gingers have a reputation of a high quality, with a lightcolor and delicate flavor. Cochin ginger has a light yellow color while Calicut is more reddish-brown; both have a delicate odor and flavor, with some lemon-like aroma. Indian ginger is mostly exported washed and dried, unpeeled or roughly peeled. African ginger is darker in color and higher in monoterpene content, giving a more pungent aroma with camphoraceous notes; it has a high oil content and level of pungency, therefore it is usually preferred for the production of oils and oleoresins.
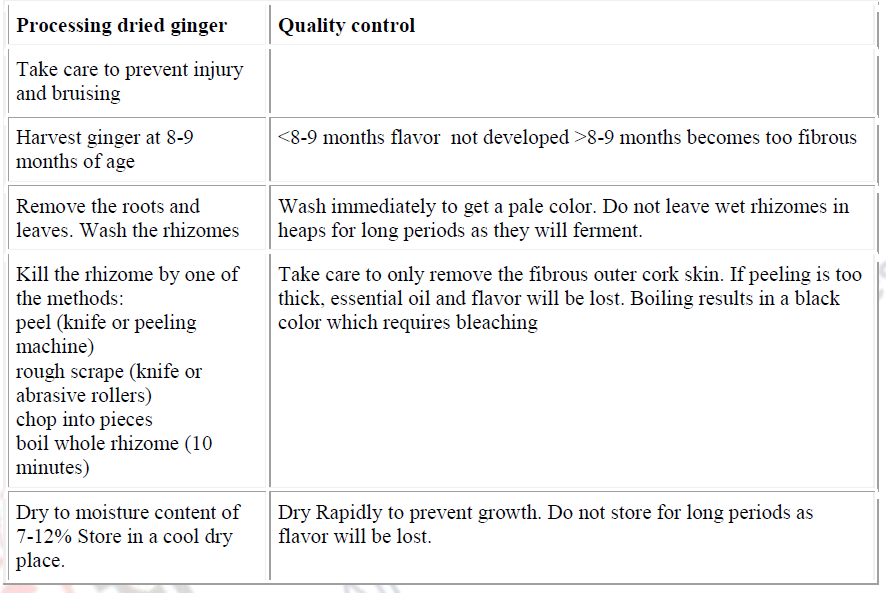
Dry ginger obtained by drying of fresh ginger comes in the spice trade for the preparationof ground ginger and extraction of oleoresin and oil. It is available in a number ofphysical forms. It can be peeled (scraped or uncoated) or non-scraped (coated or non-peeled) and sometimes partially peeled or rough scraped. In the scraped grade, the corkskin has been removed clearly without damaging the underlying tissue. Gradesdesignated as ‘bleached’ or ‘limed’ are also available. They are prepared from cleanpeeled or partially peeled whole rhizomes by treating with lime orsulphurous acid toachieve white colour. Physical grades like black ginger, splits and slices are alsoavailable. Dried ginger is prepared from mature rhizomes which have developed full aroma,flavour and pungency, and harvesting is usually carried out at between eight to ninemonths after planting. For dry ginger making, cultivars with medium-sized rhizomes withhigh curing percentage are preferred.
The processing of dry ginger involves the following steps:
- Removal of roots and thorough washing of rhizomes.
- Preparation of rhizome for drying, which involves peeling, splitting or slicing. When whole-coated rhizomes are to be dried, preparation is by immersing in boiling water for about 10 minutes. Black ginger is prepared like this.
- Sun drying: during drying, rhizomes lose moisture, about 60–70% of their weight, and achievefinal moisture of 7–12%. Jamaican ginger is clean peeled using a special knife and, after thorough washing, sun dried. Indian ginger is rough scraped, non-bleached or bleached (limed). In this, the skin is partially scraped off with a sharpened piece of bamboo. Steel knives are not used as they stain the produce. Mechanization is possible in dry ginger processing, in grading, peeling and drying. But mechanical grading and peeling produce an inferior quality produce. Most of the producing countries resort to traditional methods which employ manual labour mainly. The appearance, the content of volatile oil and fibre, the pungency level and a subjective assessment of aroma and flavour are important in the quality evaluation of dried ginger. Cleanly peeled dried ginger in the whole form possessing the best appearance generally finds a place in the grocery trade. Lower grades of clean peeled, coated whole, split and sliced types are used for blending in the preparation of powdered mixed spices. All types may be used for oil distillation and oleoresin extraction, but the coated types are the most extensively used for these purposes.
Summary
Dry ginger obtained by drying of contemporary ginger comes in the spice trade for the preparationof ground ginger and extraction of natural resin and oil, it’s on the market during a variety ofphysical forms. It will be in the buff (scraped or uncoated) or non-scraped (coated or non-peeled) and typically partly in the buff or rough scraped.They are prepared from clean peeled or partially peeled whole rhizomes by treating with lime or sulphurous acid to achieve white colour.Dried ginger is ready from mature rhizomes that have developed full aroma, flavour and pungency, and harvest is typically applied at between eight to nine months when planting.
| you can view video on Ginger: Dehydrated Ginger |