Lipids: In Born Errors of Metabolism IV
1. Objectives
- To understand the inborn errors of peroxisomes
- What are the disorders and disease associated with peroxisomal dysfunction
- How the β and ώ oxidation disorder takes place
2. Concept Map
3. Description
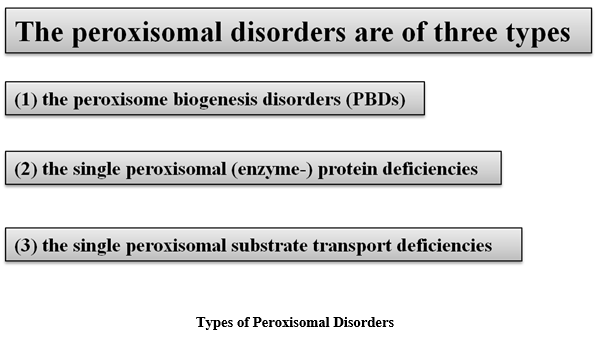
Peroxisomal Disorders
The peroxisomal disorders represent defects in peroxisomal functions leading to genetic diseases in man. The peroxisomal enzyme deficit group comprises seven different disorders of which phytanoyl-CoA hydroxylase (adult Refsum disease) and D-bifunctional protein deficiencies are the most recurrent. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy is the only disease of peroxisomal substrate transport deficiency group. The therapeutic interventions are typically restricted to X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. The most frequent adult-onset peroxisomal disorders are X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy and Refsum disease, recognized biochemically by elevated phytanate and a very long chain fatty acids respectively. Nonetheless, only ~85% of female carriers of adrenoleukodystrophy have unusual plasma concentrations and it ought to be assume in mind that distinctly unlike phenotypes of adrenoleukodystrophy can arise in one family.
2-methyl-CoA racemase deficiency presents an instance of a lately described adult-onset IEM. The clinical features are analogous to the Refsum disease and typify biochemically by the elevated concentrations of plasma pristanate. Quantifiable features include peripheral neuropathy, pigmentary retinopathy and seizures. Acute and sub-acute appearance crop up by fever, pregnancy and rapid weight loss.
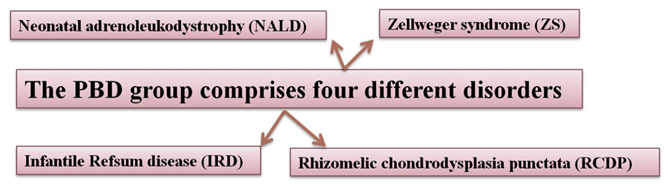
Figure 2. Examples of Peroxisomal biogenesis disorders
Cerebrohepatorenal syndrome also known as Zellweger syndrome is a congenital and rare disorder illustrated by the absence or reduction of peroxisomes in the cells of the brain, kidneys and liver that distress the aptitude to β- oxidize very-long chain fatty acids in the peroxisomes of the cell, owing to a genetic disorder in one of the numerous genes involved with peroxisome biogenesis. A number of peroxins are allied with Zellweger syndrome, including PEX1, PEX2, PEX3, PEX5, PEX6, PEX12, PEX14, and PEX26. The disorder is also known as the Zellweger spectrum occurs in one of three peroxisome biogenesis disorders. The further two diseases are infantile Refsum disease and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy (NALD).
β-Oxidation of very long chain fatty acid oxidation.
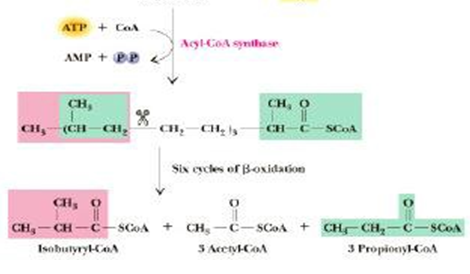
A very long chain fatty acids in which carbon atoms are 22 or more than that undergoes β-oxidation in the peroxisomes and the shortened fatty acids that undergoes β-oxidation in mitochondria.
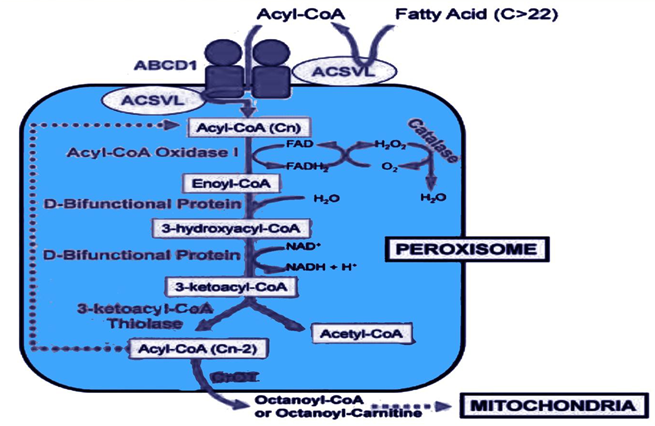
Figure 3. β-oxidation ofvery long chain fatty acidinperoxisomes
In contrast to mitochondrial β-oxidation, the preliminary dehydrogenation in peroxisomes is catalyzed by an FAD-containing acyl CoA oxidase. The FADH2 produced is oxidized by molecular oxygen, which is abridged to H2O2; thus, no ATP is generated by this step. The H2O2 is reduced to H2O by catalase [Note: Genetic defects either in the ability to target matrix proteins to peroxisomes (resulting in Zellweger syndrome —a peroxisomal biogenesis disorder) or in the ability to transport VLCFA across the peroxisomal membrane (resulting in X- linked adrenoleukodystrophy), lead to accumulation of VLCFA in the blood and tissues.]
Omega Oxidation of fatty acids
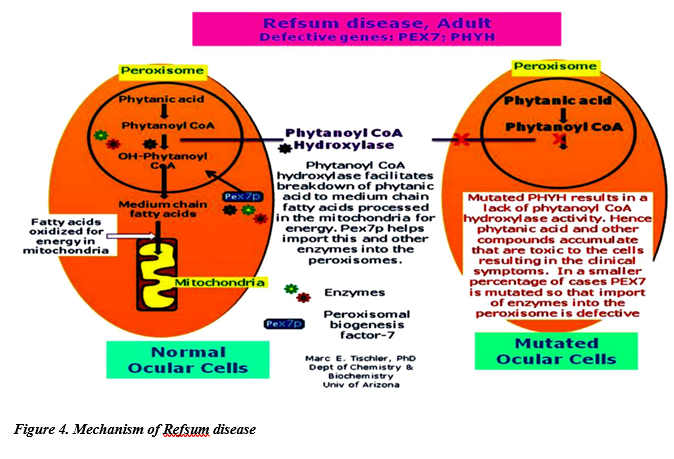
Phytanic acid (Branched-chain, 20 carbon fatty acid): This fatty acid is not a substrate for acyl CoA dehydrogenase because of the methyl group on its β carbon. Instead, it is hydroxylated at the α-carbon by phytanoyl CoA α-hydroxylase (PhyH), carbon 1 is released as CO2, and the product, 19 carbon pristanic acid, is activated to its CoA derivative and undergoes β-oxidation. Refsum disease is an autosomal and rare recessive disorder caused by the absence of peroxisomal PhyH. This results in the accretion of phytanic acid in the tissue and plasma. The symptoms are primarily neurologic, and the treatment involves dietary restriction to halt disease progression. [Note: ω-Oxidation (at the methyl terminus) also is known, and generates dicarboxylic acids. Normally a minor pathway of the ER, its up-regulation is seen with conditions such as MCAD deficiency that limit fatty acid β-oxidation.]
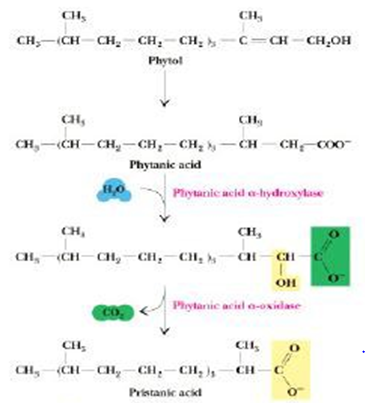
Figure 5. Oxidation of Phytol
Phytanic acid α oxidase oxidizes phytanic acid to yield carbon dioxide and pristanic acid (odd chain fatty acid) that can be consequently oxidized by β-oxidation. This process rivets hydroxylation of the α carbon, removal of the terminal carboxyl group and concomitant alteration of the α hydroxyl group to a terminal carboxyl group, and linkage of CoA to the terminal carboxyl group. This branched substrate will operate in the β-oxidation procedure, eventually yielding Acetyl CoA, Propionyl-CoA, and 2-methyl propionyl CoA (Iso-butyryl CoA, in the case of phytanic acid)
Inborn errors of cholesterol biosynthesis
Cholesterol have an important function as it is a part of membrane component as well as it is a precursor to bile acids, vitamin-D and steroid hormones.
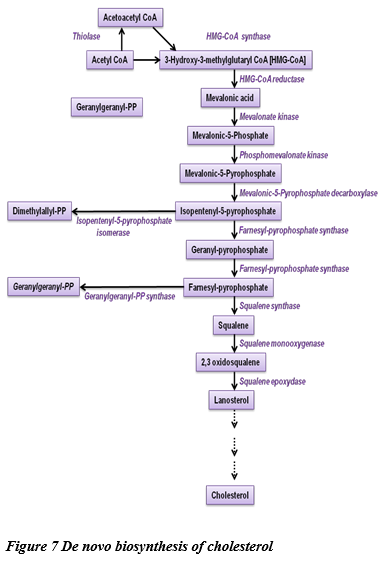
The cholesterol biosynthesis disorders have lately emerged as imperative IEM which have taught us a lot of new genetic and biochemical edifications. Despite the fact that most of the metabolic diseases are exemplified by exclusively or largely post-natal biochemical deficiencies or toxicities, cholesterol biosynthesis disorders are prominent for their relentless effects on pre-natal development.
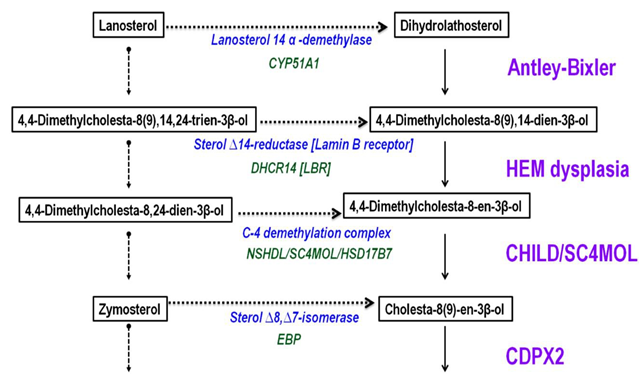
Figure 8: Synthesis of cholesterol from Lanosterol and syndromes and inborn errors of metabolism associated with them
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia also known as spelled familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH or SFH) is a genetic disorder portrayed by high cholesterol levels, exclusively very high levels of LDL (low density lipoprotein or bad cholesterol) in the blood and untimely cardiovascular illness. Individuals with FH or SFH displayed different body biochemistry and their elevated cholesterol levels are less responsive to the control methods of cholesterol frequently more efficient in people without FH or SFH (e.g. dietary modification and statin tablets). However, the high doses of statin as a treatment regimen is usually effective.
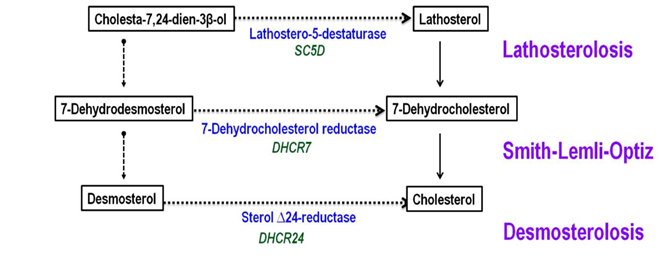
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS) is a manifold congenital anomalies (MCA) / mental retardation (MR) syndrome caused by a deficiency in the synthesis of cholesterol. SLOS is an autosomal recessive genetic state caused by the deficiency of 3 β-hydroxysterol-δ 7-reductase (7-dehydrocholesterol-δ 7-reductase [DHCR7] EC 1.3.1.21), the ultimate enzyme in the sterol biosynthetic pathway that converts 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholesterol.
Figure 9. Child with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.
Other lipid disorders
Carotenemia
In 1904, it was originally noted as Xanthosis diabetic by von Noorden, who experiential it to be well-known in the nasolabial folds and on the palms and soles. Carotenemia is a clinical condition depicted by the yellow pigmentation of the skin (xanthoderma) and augmented β-carotene levels in the blood. In most of the cases, the situation pursues extended and too much consumption of carotene-rich foods (e.g. carrots, sweet potatoes and squash). It is a frequent finding in children. The condition of carotenemia is undisruptive, but it can show the way to a mistaken diagnosis of jaundice. Carotene is a lipochrome that usually append yellow color to the skin and with the elevated blood levels of carotene; the eminence of this yellowing is amplified. When the stratum corneum is thickened or when the sub-cutaneous fat is strongly represented, carotenemia is particularly evident. The situation is more effortlessly appreciated in light-complexioned people, and can be well monitored by the yellowing of the palms and the soles in darkly pigmented individuals..
Causes
In infants and children, diet-induced carotenemia has been observed most frequently. Mothers might tempt the form by offering their infants a hefty amount of carrots via commercial infant food preparations. In addition, vegetarians are more prone to acquire carotenemia than non-vegetarians. The condition can also be associated and/or enhanced with the ingestion of carotene-rich nutritional supplements. The disease condition including anorexia nervosa, diabetes mellitus, hepatic disorders, hypothyroidism and renal diseases may also bestow ascend to carotenemia.
Lipodystrophy [Greek: Lipo for fat and dystrophy for abnormal or degenerative condition] is a condition in which adipose tissues are degraded. Specifically, Lipoatrophy signifies loss of fat from one specific area mostly face. It is also notified by a absence of circulating leptin which may lead to osteosclerosis.
Figure 10 Types of Lipodystrophy
Usually inborn errors of metabolism have more examples of autosomal recessive but there is also a condition of autosomal dominant like Lipomatosis in which multiple distinct encapsulated lipomas are present on the body due to genetic defect in HMGIC gene encoding high mobility-group protein isoform I-C.